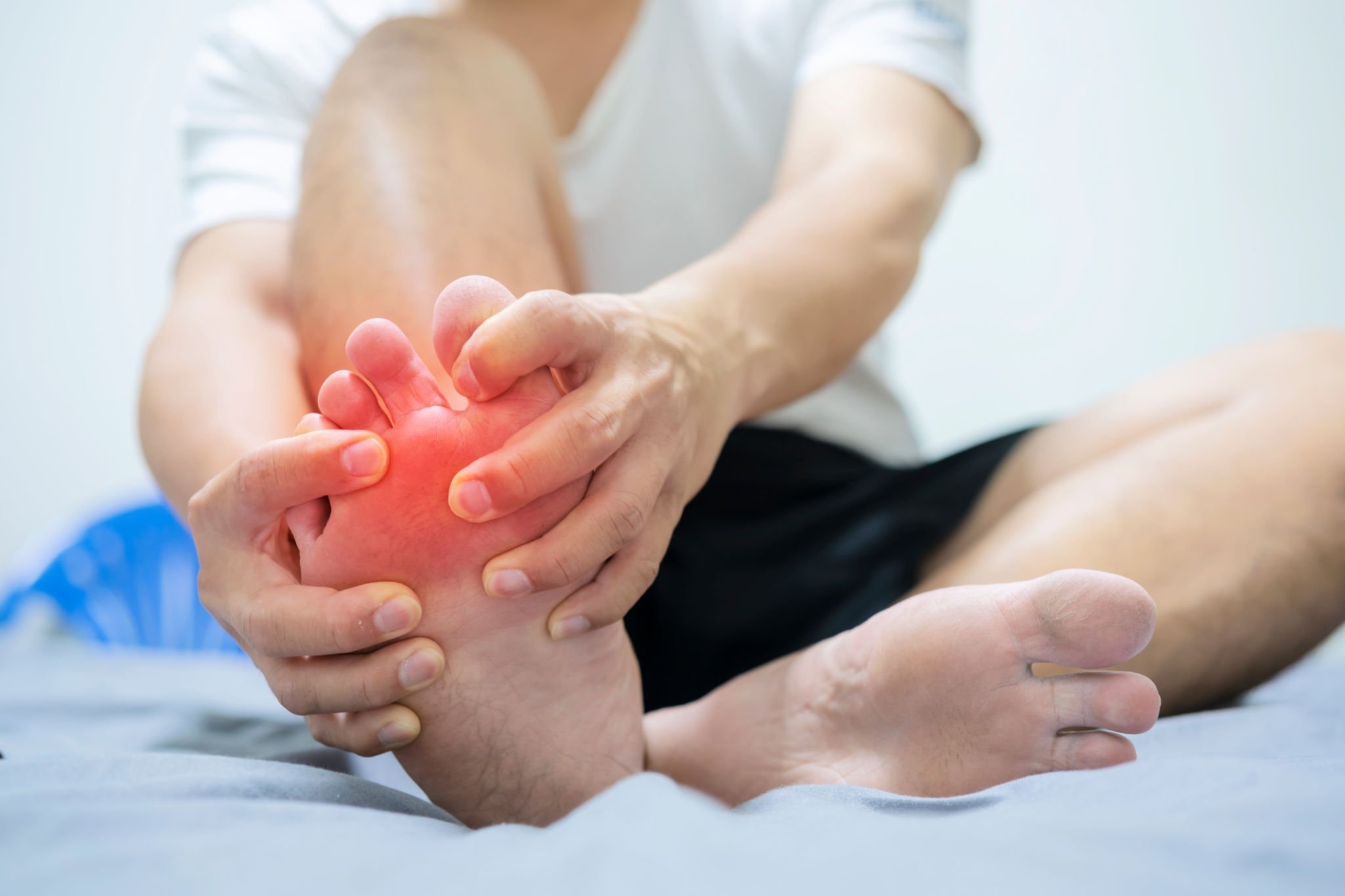
A gout is a common form of arthritis that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, which leads to painful and swollen joints. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of gout.
What causes gout?
Gout is caused by a buildup of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally filtered out by the kidneys and excreted in the urine. However, in some people, the body produces too much uric acid, or the kidneys are unable to filter it out efficiently. As a result, uric acid can build up in the blood and form crystals, which can accumulate in the joints and cause inflammation.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gout, including:
- Diet: Foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can increase the production of uric acid in the body.
- Genetics: Gout tends to run in families, and certain genetic factors can increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes, can increase the risk of gout.
- Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics and aspirin, can increase the production of uric acid in the body.
What are the symptoms of gout?
The most common symptom of gout is sudden and intense pain in the affected joint. The pain can be accompanied by swelling, redness, and warmth in the joint. Gout usually affects the big toe, but it can also affect other joints, such as the ankle, knee, and wrist.
Gout attacks can last for a few days to a few weeks, and the pain can be severe enough to make it difficult to walk or use the affected joint. Some people may also experience fever and chills during a gout attack.
Over time, gout attacks can become more frequent and can lead to joint damage and deformity.
How is gout treated?
The treatment of gout usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. The goals of treatment are to relieve pain and inflammation during an acute attack and to prevent future attacks.
Medications commonly used to treat gout include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs can relieve pain and inflammation during an acute attack.
- Colchicine: This drug can also relieve pain and inflammation during an acute attack.
- Corticosteroids: These drugs can be taken orally or injected into the affected joint to relieve pain and inflammation.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can also help prevent gout attacks. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet that is low in purines and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limiting alcohol consumption.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Exercising regularly.
In some cases, medication to lower uric acid levels in the blood may be necessary to prevent future gout attacks. These medications can include allopurinol, febuxostat, and probenecid.
Conclusion
gout is a painful and often debilitating form of arthritis that is caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. While gout cannot be cured, it can be managed with a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. If you think you may have gout, it is important to see a doctor for a diagnosis and treatment.